If you’ve ever looked at a website’s source code, you’ve probably seen strange symbols like <p>, <title>, <link>. These are structural elements that form the foundation of the web. But what exactly is a tag in HTML and why is it so important? Let’s break it down in simple terms — no technical overload.
What It Is and Why It Matters
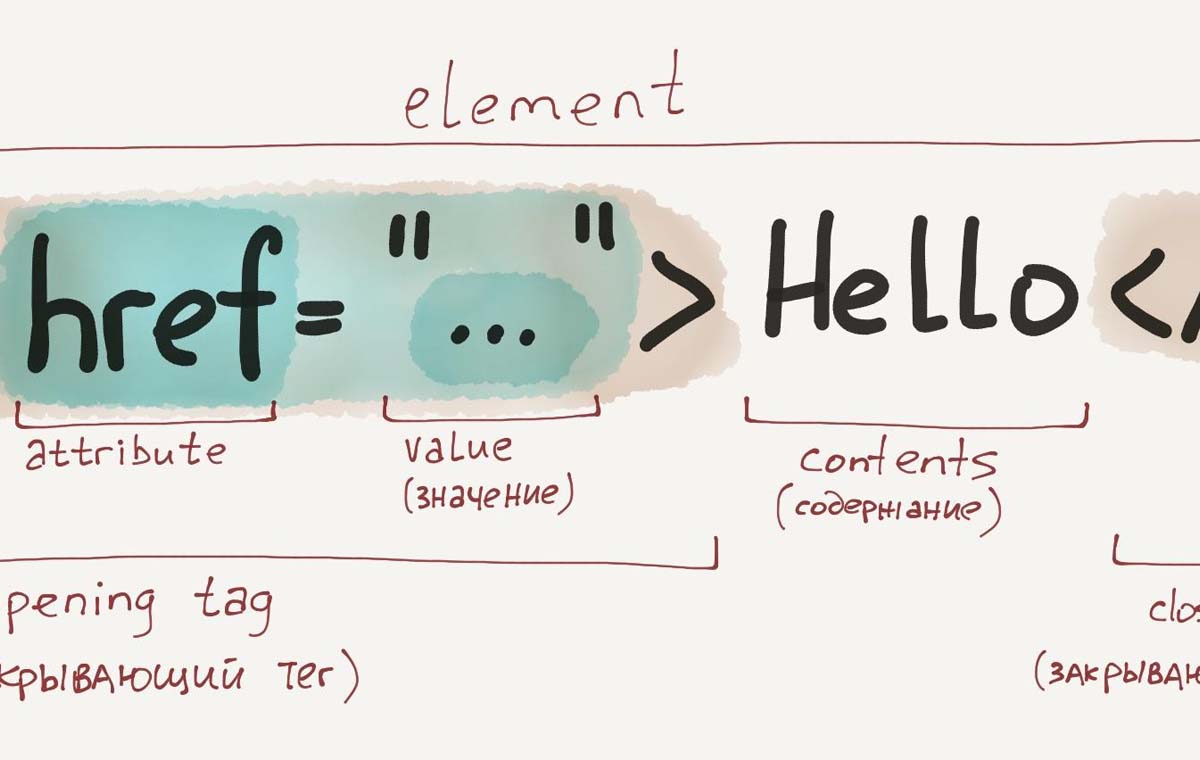
HTML markup is like the skeleton of any digital platform. It defines how elements are arranged and interact — headings, images, tables, forms, and more. So what is an HTML tag? Simply put, it’s a command that a browser reads and converts into a visible object: text, image, or link.
Tags are either paired (opening and closing) or standalone. Paired tags look like this: <h1>Title</h1>. Standalone tags are written in one line, like <br> to add a line break.
Example: How It Looks and Works
Let’s look at a simple example — a paragraph. Its structure is:
<p>This is a regular paragraph of text on the website.</p>Here’s how you insert an image:
<img src="photo.jpg" alt="Sunset landscape">This is a self-closing tag. It includes parameters — the file path (src) and a description (alt). This tells the browser: “Place an image here and show what it represents.”
What Is a Tag in HTML?
An HTML tag is the foundation of web content. Every element in a digital document is created using these markers. They’re like building blocks: some define text, others lists, others input fields.
If you remove all markup, nothing remains — no headings, no links, not even an empty paragraph. That’s why understanding tags is key to building a functional and logical website structure.
What Is the <link> Tag in HTML?
The <link> tag is one of the technical tools that connects external resources — most often stylesheets. Example:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">When the browser sees this tag, it loads the CSS file and applies the design: fonts, colors, spacing, and other visual elements.
What Is the <title> Tag in HTML?
The <title> tag sets the document’s title. It’s invisible to the user on the page but appears on the browser tab and in search results.
<title>Sports Nutrition Store</title>This is the text users see in their browser tab. Search engines also read it to understand what the page is about — so this tag affects both perception and SEO.
Main Functions of HTML Structure
Here’s what HTML tags help accomplish:
- Logical document structure: Tags organize content into headings, paragraphs, lists, tables, and more — making content easier to read for humans and machines.
- Visual rendering in browsers: Tags tell the browser how to display each element — whether it’s text, an image, a button, or a form.
- Semantic meaning: Tags like <header>, <nav>, <footer> explain what each block is for — not just how it looks.
- SEO optimization: Search engines use HTML structure to evaluate page relevance. Well-formatted headings and meta tags help with indexing and ranking.
- Interaction with external files and scripts: Tags allow integration with stylesheets (CSS), JavaScript, fonts, and other resources — making the site interactive and visually appealing.
Without these code markers, the digital environment would be chaotic and unstructured. With them, it becomes meaningful.
Supporting Elements and Their Role
Besides the basic tags, HTML has auxiliary tags that play important roles behind the scenes. For example:
- <meta> — tells the browser what character encoding to use
- <script> — connects external JavaScript files
- <link> — loads external CSS stylesheets
- <style> — allows inline CSS styling
- <noscript> — appears if scripts are disabled in the browser
Although these elements aren’t visible on the screen, they greatly influence appearance and functionality.
How to Use This in Practice
If you’re a beginner, don’t worry. Understanding this is easier than it seems. Start with the basics: create a simple webpage, add some text and headings, maybe a bit of styling. The key is not to be afraid to experiment.
Step by step, you’ll learn what each part of the structure does and how to use it to achieve your desired result.